Beijing Siheyuan Building
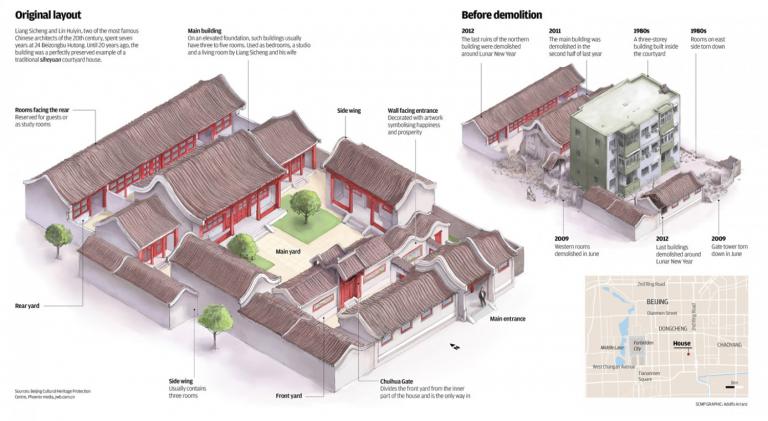
3 min readIn Northern China,one major characteristic of the traditional residential houses is the courtyard,which is the center of the house.A courtyard house is built on the basic principle of having a firm,solid exterior blend in with a vacant,spacious interior.The house is constructed on an invisible axis,around which the different functional rooms are built.Beijing’s courtyard houses(siheyuan)were predominantly situated within the capital city.Its architectural structure fit perfectly into the official model that was typical in the capital,which deemed it necessary to fulfill certain religious and moral principles that were essential to maintaining order in a traditional family.

A typical Beijing courtyard house has an invisible north-south axis in the layout of the house.The main gate of the house is placed at the southeasterr corner of the house.In accordance with the principles of feng shui and the Eight Diagrams,this is considered the most auspicious direction and could bring wealth to the household.Upon entering the house,one is greeted by an exquisitely crafted screen wall,which,in the past,carried the function of warding off evil spirits.It also helps in creating space and maintaining one’s privacy,meeting feudal family’s requirements on privacy and introverted psychological characteristics.
To the north of the front yard is the second and inner gate of the compound,which is also situated along the axis.The two festoon pillars hanging on bothsides are exquisitely carved with elaborate floral designs,making it the most prominent design element in the entire courtyard compound.The festoon gate acts as a divider between the outer and inner courtyards.In a courtyard with a hall and several sections,it is behind the hall as the door to sleeping room in the”hall in front and sleeping room behind”pattern.
Behind the festoon gate is the main living compound of the courtyard house.Here,the courtyard is beautifully landscaped with trees and other plants,creating a tranquil and comfortable living environment.To the north of the courtyard,the south-facing principal room makes up the main building of the courtyard house.In accordance with Ming and Qing building regulations for residential houses,there are usually three rooms with two side rooms flanking the principal room.On both sides of courtyard are the wing-rooms.
Behind the principal room,there is a small courtyard,with a row of rooms forming the last section of the courtyard compound.

Within a courtyard compound,all the rooms are assigned to the members of the family according to seniority.The principal rooms are for the senior members of the household.Within the principal room,an altar and the ancestor tablet are put in place.The side rooms are for the junior members.
Servants with the lowest status could only live in servant’s rooms in the outer yard,and maidservants lived in backrooms.The other rooms must not surpass the principal rooms in terms of their areas,heights and interior decorations.
This gives prominence to the idea of showing respect to the ancestors and acknowledging the power and influence of the patriarch,forming clear principal-subordinate,center-side and inside-outside relationships and making the principal room not only the main activity room of the family,but also a symbol of the family’s spirit.
One advantage of a courtyard house is that it could be infinitely expanded.
With the increase in the number of family members or out of living needs,more rooms can be added,with more courtyards created.More courtyards and rooms can also be built beyond the existing compound,with corridors and walls connecting the annexes to the main compound.This construction mode for residential houses is in keeping with China’s ancient family tradition and its development.
Other than those in Beijing,the courtyard houses in south Hebei,Shanxi,Shaanxi,Henan and other places are long and narrow,built in the north-south direction,shielding the interior of the house from sunlight.In the northwestern provinces, such as Gansu and Qinghai, the houses have thick and high walls to keep away sand and resist the cold weather. In the northeastern provinces, where the land is vast with a small population and a cold climate, there is the need to maximize the intake of sunlight. Hence, the houses there are usuallybig and spacious. Thus, in various places in China, the courtyard houses take on different characteristics in accordance with the environments they are in.