ADORNMENT
4 min readJade has been cherished by the Chinese as a symbol of many virtues.Its hardness suggests firmness and loyalty, and its luster projects purity and beauty. Typical subjects are carvings of flowers, animals, vases, and human figures.
Jade pendant of the Hemudu Culture, one of the earliest discovered so far.
In the Neolithic Age, when people gradually recognized colored stone similar to jade in choosing stone for making implements, they used such stone to make implements, ornaments and sacrificial offerings. The colored stone turned items can be called the embryonic form of jade artworks, which can be traced back to the Hemudu Culture in China. By the middle and late years of the Neolithic Age, jade-carving had been detached from stone ware making to become an independent handicraft. China is a major jade producer in the world. According to Shan Hai Jing (Book on Mountains and Seas), an ancient writing about geography, there are more than two hundred places where jade is found, which means that the source of jade is inexhaustible in China. Hetian of Xinjiang is a well-known place of jade origin in China; Jiuquan of Gansu, Lantian of Shaanxi, Dushan and Mixian of Henan, and Xiuyan of Liaoning are also rich in quality jade resources.
Animal-mask patterned cong(long hollow piece of jade) of the Liangzhu Culture,8.8 cm high, about 6,500g in weight.
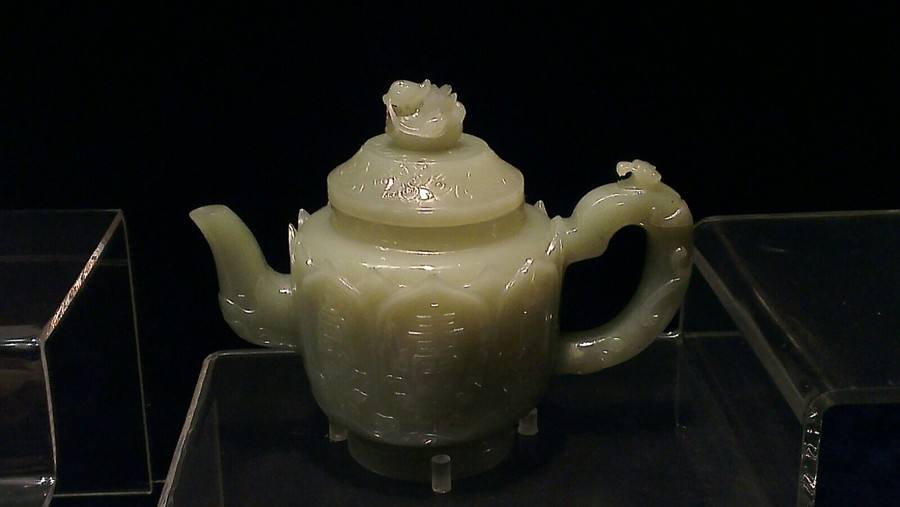

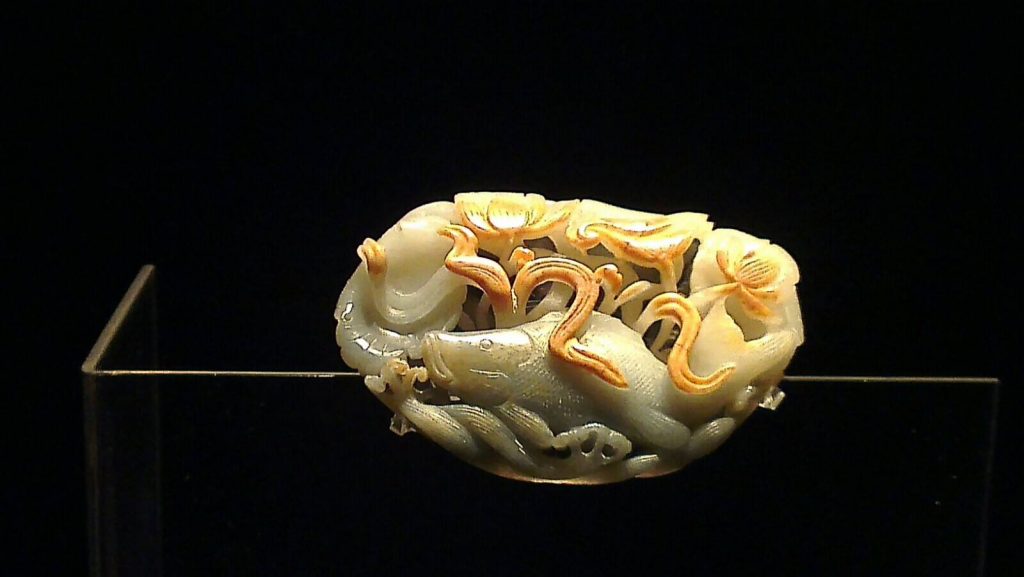
Western Han-dynasty jade cladding,a funerary object carved out of a whole piece of jade into a dozen or so pieces for each correspondent part of the face.
Generally, the procedure of jade carving includes jade observation, designing, opening, piercing, cutting and polishing. Tang Rongzuo,a collector in the late Qing Dynasty, once wrote a book entitled Of Jade in which the working procedure, methods and implements in carving jade ware are illustrated with twelve color drawings. As viewed from the perspective of craft,a jade artwork with superb workmanship excelling nature is not made by carving, but by grinding with water using minerals such as emery, silicon, garnet, etc. that are harder than jade. Therefore the process of jade making is called jade rolling or jade grinding. While the skills in grinding jade are superb, the tools used are simple and crude. The primitive implement used is simply a revolving round disk called tuo(emery wheel), which is used to move emery which rubs, smoothes and polishes jade. During the Neolithic Age and the Bronze Age when ironware was not yet been invented, tools used were largely made from wood, bamboo, animal bone compounded with sandstone. Until the modern times, Chinese people always used traditional tools in the manufacture of jade artworks such as wire saw, round disc made of steel and wrought iron, etc.
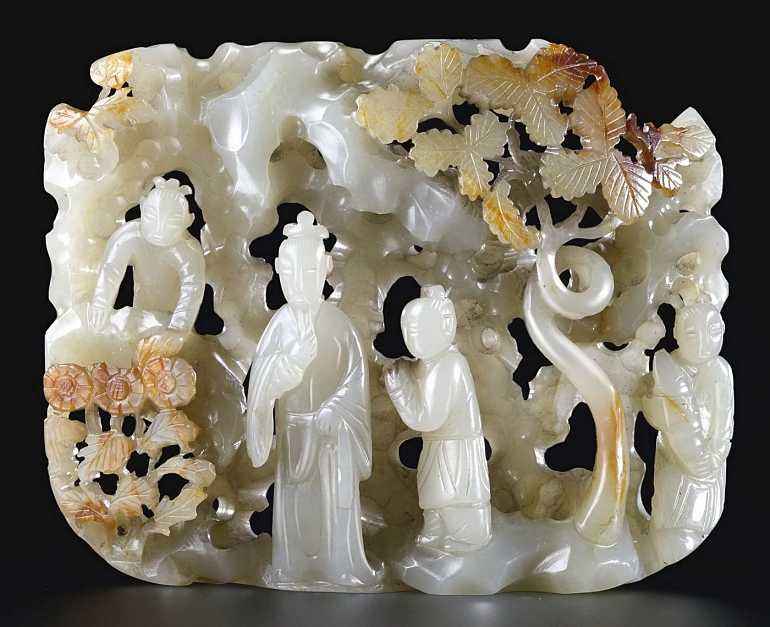

Jade Carving: an illustration in Tiangong Kaiwu(Exploitation of the Works of Nature).
Jade carving was highly developed in the Han and Tang dynasties. Funerary jade was the most typical of the Han jade articles. It was made in the belief that the jade would keep the body from decaying. Funerary jade articles include jade apparel, nine orifice stopper, etc.. The jade apparel was divided into gold inlaid, silver inlaid and copper inlaid prepared in the light of the identity and official title of the dead. The nine orifice stopper was used to cover the nine orifices of the ears, eyes, mouth, nostrils, anus and genital in the hope that the body would not decay as the vital energy was preserved by the orifice stoppers. As regards jade articles for ornament, jade galloping steeds, jade bears, jade eagles, and jade bi xie(a legendary holy beast, looking like a lion, with two wings, said to drive out evil things), were manufactured in the Han Dynasty. These artworks were practical in shape, exquisite in workmanship, and unconstrained in style. The Tang Dynasty jade artworks, affected by painting, sculpture, and the art of the Western Region, were represented by the eight-petal pattern jade cup and animal mask agate cup, in a style dignified and stately, full of Western Region flavor.
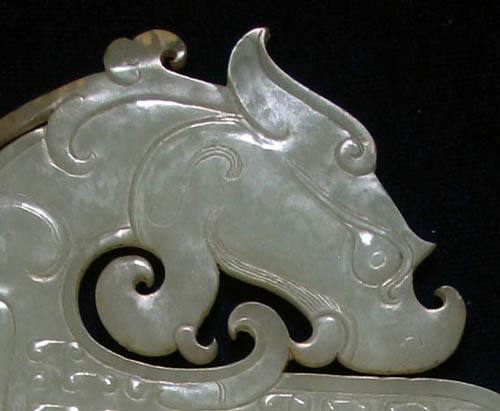

Du Shan Yu Hai(partial).
Du Shan Yu Hai(Extra large jade of Dushan),a jade carving of Yuan Dynasty,70 cm high,493 cm in circumference.
Circumstances change with the passage of time, from the Song-Liao-Jin Period the function of jade objects as sacrificial vessels was weakened, and instead, jade artworks close to practical life, some for ornaments and some for daily appreciation dominated with the prosperity of urban economy. In the Song Dynasty, the “qiao se”(wise use of color) process was initiated by which various objects extremely refined could be carved in the light of the natural luster and color of the jade material, and its texture and shape.
Yu the Great Curbing the Flood,a jade carving of Qing Dynasty, the world’s largest jade piece,224cm high,96 cm wide, more than 5,000kg in weight. It is now kept in Palace Museum.
The Yuan, Ming and Qing dynasties were the heyday of jade carving. Du Shan Yu Hai(extra large jade bowl of Dushan) and Da Yu Zhi Shui Yu Shan(Jade Mountain: Yu the Great Curbing Flood) were two representative pieces of the time. The artwork DuShan Yu Hai was carved following the natural shape of the jade material to form a scene where auspicious animals swimming at will over the waves, reflecting considerably the heroic spirit of the Yuan people. The work Da Yu Zhi Shui Yu Shan manifests the influence of literati painting on artworks taking the Song Dynasty painting Yu the Great Curbing the Flood as master copy.








