General Linguistic Characteristics
2 min readChinese,together with Tibetan and Burmese and the many tribal languages of South andSoutheast Asia,belongs to the family of Sino-Tibetan languages.Besides a core vocabulary and sounds,Chinese and most related languages share the features that distinguish them from most Western languages.
·All varieties of Chinese are tonal.This means that each sylable can have a number of different meanings depending on the intonation with which it is pronounced.For example,Mandarin has four tones,Cantonese has nine tones and Taiwanese has seven tones.
The major varieties of Chinese are mutually unintelligible,but most people in China who don’t speak Mandarin as their first language,can speak or at least understand it a bit.
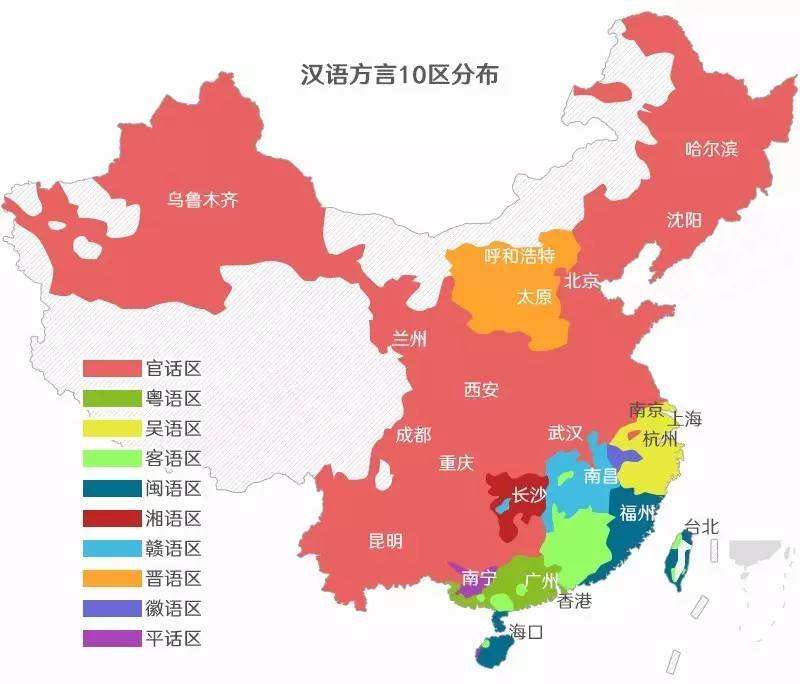
Each of the major varieties of Chinese has numerous dialects.For example,Mandarin can be divided into northern,southern and southwestern dialects,which are more or less mutually intelligible.
Language vs.Dialects
Spoken Chinese comprises many regional variants,generally referred to as dialects.
However,the mutual unintelligibility of the sub-varieties is the main ground for classifying them as separate languages or dialect groups.Each dialect group consists of a large number ofdialects,many of which may themselves be referred to as languages.The boundaries between one so-called language and the next are not always easy to define.Because each dialect grouppreserves different features of Middle Chinese(dating back to early or even Pre-Tang times),they have proven to be valuable research tools in the phonological reconstruction of Middle and even to some extent its ancestor,Old Chinese.Most Chinese speak one of the Mandarin dialects,which are largely mutually intelligible.








