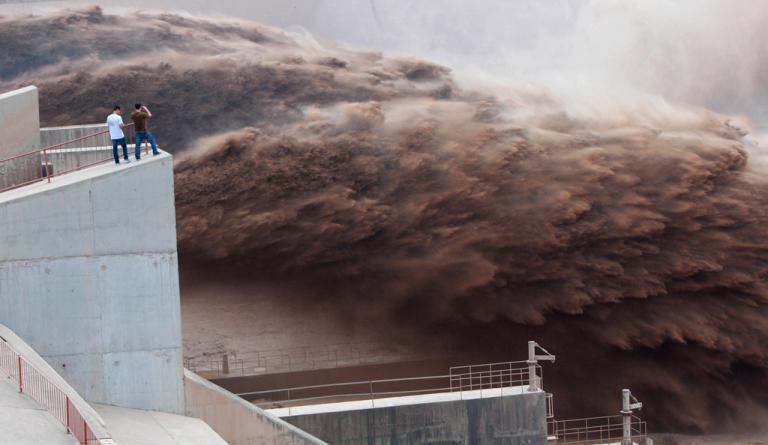
The Winding Yellow River
10 min read“See how the Yellow River’s waters move out of heaven, entering the ocean, never to return.”With only a few words (14 in Chinese),”Fairy Poet”Li Bai in the Tangdynasty portrayed mighty, vast water surging forward in his poem Bringing in the Wine. While in another poem Out of the Great Wall written by renowned border poetWang Zhihuan, the sentence”the yellow sand rises as high as white cloud; the lonel town is lost amid the mountains proud.”was even the all-time masterpiece in singing the Yellow River.
Theword of Huanghe(the Yellow River) was first appeared in Han Works. written byBan Gu, the famous historian in the Eastern Han dynasty (25-220). Before the Han dynasty (206 BC-220AD), the word “He”(meaning river in English) refers exclusively to the Yellow River, which is recorded in detail in many ancient classic literatures such as Esteemed Documents: Discussion on the Tribute of Yu,A Chinese Bestiary, Wei Feng of the book of songs. The Analects of Contrcius. The works of Mencius, The Annals of Spring and Autumn Period, Remarks of Monarchs and so on. Erya: Explaining Rivers gave the following explanations about why the river is given the name “Huanghe”(the Yellow River): the Yellow River originates from Kunlun Mountain and it’s limpid at the beginning; however, after it absorbs over 1,700 rivers, the riverbegins to take on a yellow color. Hence, we can draw the conclusion that the Yellow River got its name from the color of its water. But it was not until the Song dynasty (960-1279) that it was commonly called “Huanghe”(the Yellow River).
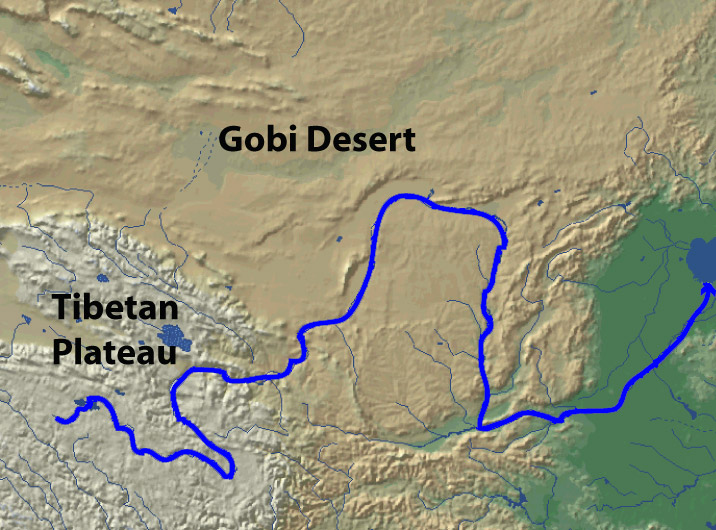
1. The Winding Yellow River
The Yellow River, traversing the Chinese territory, has a length of 5,464 kilometers of its mainstream, which is only next to Yangtze River and is the secondlongest river in China. The long river course and vast drainage area give the Yello River its unique grandeur which distinguishes it from other rivers. The Yellow River is divided into three sections,i.e. the upper reaches, the middle reaches and thelower reaches, according to the different topography and relief of the differentareas that the Yellow River courses through and other factors such as the water conditions.
1) The Upper Reaches of the Yellow River
The upper reaches of the Yellow River are a segment starting from the source in Bayan Har Mountains and ending at Hekou Town in Tuoketuo County in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region of China. This segment has a total length of 3,472 kilometers and total basin area of 386,000 square kilometers, accounting for 51.3% of the total basin area of the Yellow River. Along this length, the elevation of the Yellow River drops 3,496 meters. There are 43 large tributaries joins the Yellow River in the upper reaches, whose total flux accounting for 54% of that of the Yellow River; however, the sediment load that the upper reaches carry to the lower reaches only accounts for 8% of the total sediment load of the Yellow River every year. Large amount of water and small amount of sediment are the main characteristics of this section. Therefore, the upper reaches are also seen as the main source of clean water of the Yellow River. The river course of the upper reaches takes the shape of “S”under the influence of Anemaqen (Amne Machin) Mountains, Xiqing Mountains, Qinghai-Nanshan Mountains. According to the different characteristics of the river courses, the upper reaches can be further divided into three sections: the source, valley and alluvial plain sections.
The source section is the section from Kari Qu in Qinghai Province to Longyang Gorge in Guide County of Qinghai Province. It starts from Kari Qu, coursing throughSungsuk Sea, Zaling Lake and Eling Lake to Maduo County, and then flows by Anemaqen (Amne Machin) Mountains and Xiqing Mountains, finally reaching Guide County in Qinghai Province after flowing through Longyang Gorge.
This section of river flows largely on the plateau with an elevation of three orfour thousand kilometers and along the river there are numerous lakes, swamps and grasslands. In this area there also is the largest plateau fresh water lakes group of the world-Tibetan Plateau fresh water lake distribution area which is represented as Eling Lake and Zaling Lake. The lake area is of clear water, steady current and large water volume, which enables this section of the Yellow River to have clear and large amount of water.
From Maduo County in Qinghai Province to Maqu County in Gansu Province, the Yellow River flows through the ancient basin and knolls between Bayan Har Mountains and Anemaqen (Amne Machin) Mountains. Most part of the river course here is broad.
And the river also crosses some valleys here and there; the section from Maqu County in Gansu Province to Longyang Gorge in Guide County in Qinghai Province is of dangerous terrain, with many high mountains and deep valleys along its way. The drop of elevation here is very large and the Yellow River, coursing in these mountainsand valleys, flows very rapidly, therefore it is also rich in waterpower resources here. In this section the Yellow River also absorbs Baihe River and Heihe River which originate from Minshan Mountain in Sichuan Province, making it more powerful and mighty.
The valley section is between two famous gorges on the Yellow River-Longyang Gorge in Qinghai Province and Qingtong Gorge in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region. Onthis section there array 20 gorges like Longyang Gorge, Jishi Gorge, Liujia Gorge, Bapan Gorge, Qingtong Gorge and so on. Steep cliffs live both sides of the river.
The riverbed gradually narrows down and the drop of elevation enlarges obviously,s the flow in this section is extremely turbulent and fast. The section from Guide County to Lanzhou City is one of the three sections in the Yellow River Basin wherethe tributaries are most concentrated, in which there are important tributaries such as Taohe River, Huangshui River etc, greatly enriching the water volume of the Yellow River. The mainstream of the Yellow River from Longyang Gorge to Xiaheyan of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region is of the richest waterpower resources in the wholeYellow River Basin, and also one of the important locations to build hydroelectric plants in China.
Alluvial plain section is from Qingtong Gorge in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region to Hekou Town in Tuoketuo County in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region. After emerging from Qingtong Gorge, the Yellow River flows to the northeast along the northwestborder of Ordos Plateau, and then turns eastwards to Hekou Town. In this section, the regions along the river are mostly deserts and grasslands, with very few tributaries. The riverbed in this section is flat and the currents also slow down gradually. Therefore part of the sand and silt carried by the water deposit near the banks and large stretches of alluvial plain at the two sides are formed. The famous Yinchuan Plain and Hetao Plain are just formed in this way. The plains a long theYellowRiver, while benefiting fromthe irrigation of the river, also have to endure the disasters the Yellow River brings, such as ice run and floods.
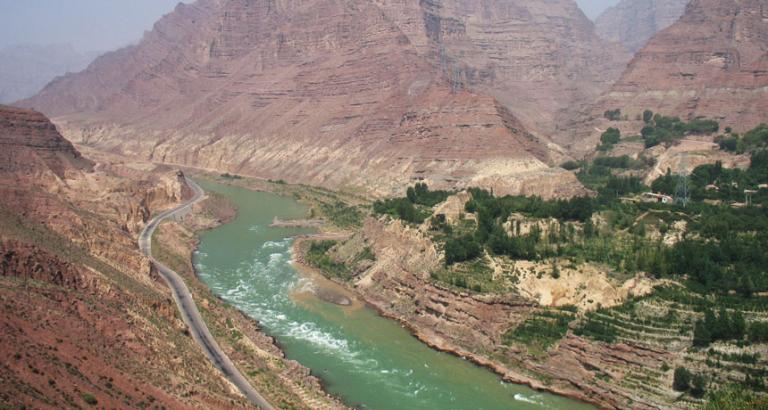

2) The Middle Reaches of the Yellow River
The part of the Yellow River between Hekou Town in Tuoketuo County in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region and Taohuayu in Zhengzhouin Henan Province constitutes the middle reaches of the river. The middle reaches have a length of 1,206 kilometers and basin area of 344,000 square kilometers, accounting for 45.7% of the total basin area of the Yellow River. Since most part of the middle reaches are on the North China Plain, the total elevation drop is only 890 meters. In this course there are over 30 large tributaries entering the Yellow River and the water volume is increased by 42.5% of the total water volumeof theYellowRiver.
Half way in this section, the river flows past the largest loess area in the world-the Loess Plateau, where substantial erosion takes place, and make this are the major source of the sand and silt in the Yellow River. In fact, the sand and silt amount of the Yellow River added in this area accounts for 92% of the river’s silts. Numerous tributaries carry large amount of sand and silt into the Yellow River, making the originally clear water extremely muddy and the Yellow River the most sediment-laden river in the world.
In the middle reaches of the Yellow River there is a valley called Jinshan Valley, which stretches from Hekou Town to Yumenkou, and is the longest series of continuous valleys on its main course. Most of the tributaries of the Yellow River in this section pass the Loess Plateau where soil erosion is so serious that hasbecome the main source of silts in the Yellow River. The average sediment load of the YellowRiver is 1.6 billion tons per year, among which 900 million tons are from this area. The drop of elevation in the valley section is also very large, with abundant stored waterpower resources, and it is the second largest area to build hydroelectric power plants on the Yellow River. In the lower part of the valley section there is a famous fall called Hukou Waterfall, with a tunnel of only 30-50 meters wide. In the low water period, the drop of water surfaces is about 18 meters, and in the high water seasons, water rushes down from high above like a herd of galloping horses, looking quite magnificent and spectacular. Therefore, Hukou Waterfall attracts visitors fromall over the world.
Upon the arrival at Fenwei Plain, the Yellow River widens up and the currents slowdown. The two sides of this river course are the important agricultural areas of Shaanxi and Shanxi provinces respectively-Weibei Arid-plain and Jinnan Loess Tableland. In this section the Yellow River receives the important tributaries like Fenhe River, Luohe River, Jinghe River, Weihe River, Yiluo River, Qinhe River and soon, all of which carry large amount of sand, making this section one of the major sources of sand in the lower reaches of the Yellow River. Of all the years, the sediment load of these tributaries averages over 550 million tons per year. In the 132.5 kilometers river course from Yumenkou to Tongguan (i.e. the small north mainstreamof the YellowRiver), the scouring and silting variation is specially acute, and the direction of the torrents changes frequently. Near Tongguan, the river course becomes extremely narrowunder the constrictions of the high mountains the water has to squeeze through the valley that is only 1,000 meters wide.
The section between Sanmen Gorge and Taohuayu can be divided into two parts with Xiaolangdi as the border: above Xiaolangdi is the last valley section on the mainstreamof the YellowRiver, which courses between Zhongtiao Mountain and Xiaoshan Mountain; under Xiaolangdi, the river valley gradually widens up, which is thetransition area that the Yellow River enters plain area from mountain area.
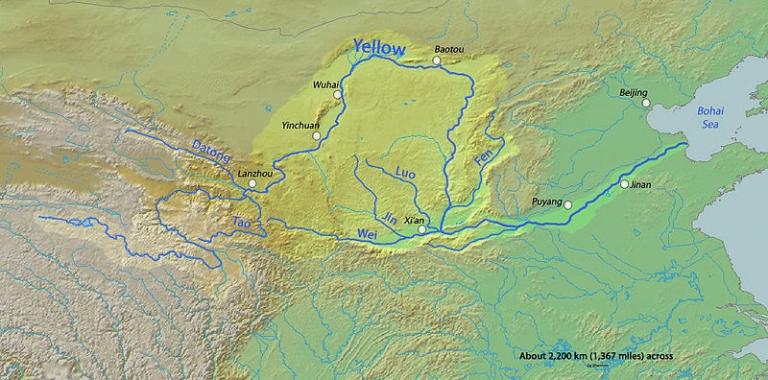
3) The Lower Reaches of the Yellow River
The section from Taohuayu of Zhengzhou in Henan Province to the river mouth at the sea is the lower reaches of the Yellow River, which is 786 kilometers long and drains an area of 23,000 square kilometers, accounting for only 3% of the total basin area. The drop of elevation in this section is 93.6 meters. There is not much water added in this section; except Dawen River which joins the river through Dongping Lake, there is no large tributary entering this section of the Yellow River. After entering the plain area, the silts carried from the upper and middle reaches begin to deposit as the current slows down. As time goes by, more and more sand and silt accumulate, resulting in the rise of the riverbed and also the water level of the river. In order to prevent the Yellow River form breaching, people have to build the levees higher. Therefore, the lower reaches of the Yellow River become the world-famous “river above ground”. The riverbed of Yellow River near Kaifeng in Henan Province is almost of the same height as landmark construction-Kaifeng Iron Tower. Although this kind of scenery looks grand and spectacular, there is much hidden trouble in it.
Although the YellowRiver is confined to a levee-lined course, it still possesses superior power, and becomes the natural border of Haihe River Basin and Huaihe River Basin.
The lower reaches of the Yellow River, except the area from Dongping Lake inHenan Province to Jinan in Shandong Province where there are a few hills as barriers, all depend on the man-made levees to keep the water in the river. The total length of levees in this section of Yellow River is over 1,400 kilometers. The long course, high water level and surging currents, are all the deepest worries of the people living along the Yellow River. And the reality justifies the necessity o people’s worry. Throughout the history, the levees of the lower reaches of the Yellow River has been breached for many times, and the river water, just like a horse running wild, rushed onto the surrounding lands in all directions, releasing its long-oppressed energy. The floods rendered the people homeless, and at the same time destroyed numerous farms and claimed countless lives. All these painful memories are the deepest wound in the heart of the Chinese people.
Besides the floods, another important natural disaster in the lower reaches of the Yellow River is ice run. The occurrence of ice run is because the lower reaches of the YellowRiver flows from the southwest to the northeast. In winter, the northis cold and the section in the north is first frozen, which obstructs the flow of the currents, meanwhile it is still warm in the south and the water flows to the northeast continuously. Therefore, the water volume in the frozen section is larger and larger and when the levees at last cannot stand the pressure and are breached, the water mixed with lumps of ice overruns in all directions, thereupon ice run occurs. Since ice run usually will result in ice dam blocks and dike-bursting, it imposes severe damage on the lives and properties of the people living along the river.
The section under Lijin is called the river mouth section of the Yellow River habitually. There are continuous sediment deposits at the river mouth of the Yellow River, and the area and height of the deposits are also increased continuously aftermany years. The river mouth today is in the border area of Gulf of Bohai and Gulf of Laizhou, which is a man-made new river course through changing the course of the Yellow River by the Chinese government in 1976. In the recent 40 years, the sediment load that the Yellow River carried to the river mouth area averaged about 1 billion tons per year, and with these sediments, the Yellow River would increase its land acreage every year about 25-30 square kilometers. Howastonishing the power of nature is!









