What is the route of the Ancient Silk Road?
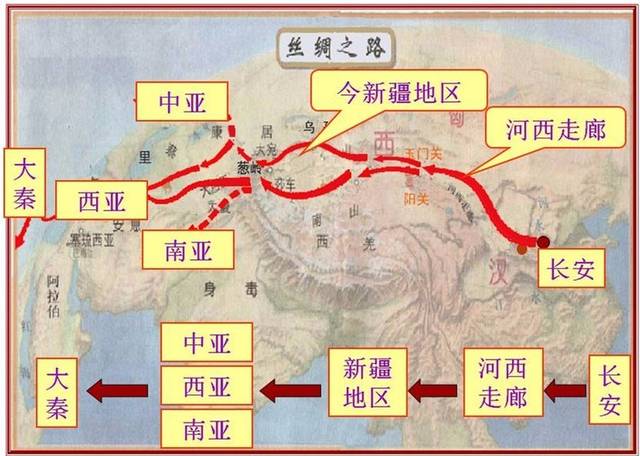
2 min readThe Han Dynasty Silk Road began from the Han capital,Chang’an ,the present site of Xi’an .The route took traders westwards into Gansu Province where it passed through Lanzhou ,Tianshui and Jiuquan .It advanced along Hexi Corridor until it reached Jiayuguan ——the giant barrier of the Great Wall and the first key point of the route:Dunhuang .
When the Silk road entered Xinjiang from the Hexi Corridor,it broke into three main roads.The southern road ran west along the northern foot of the Kunlun.Mountains and on to Kashgar .It then went over the Pamirs and arrived in India;or it passed through Afghanistan and Russian Central Asia and reached Arabia or the coast of the Mediterranean.
The central road extended west along the southern foot of the Tianshan Mountains and Aksu .It then crossed the Pamirs and continued on to Mari in Russia. The northern road went along the northern foot of the Tianshan Mountains and reached the Yili River Valley before it advanced to areas near the Black Sea.
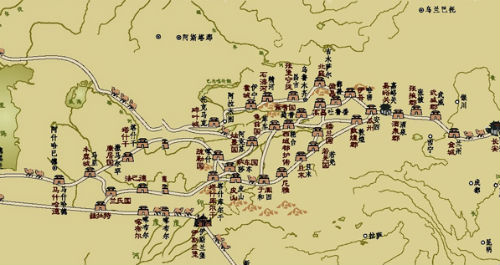
The three routes of the Silk Road ran between mountain ranges,traversed desolate desert areas,and wound over snow-capped peaks in Xinjiang.It was the only way for China to get in touch with the West between the 2nd century B.C.and the 10th century A.D.Although sections of the Silk Road have long been buried by deser sand,the dry local climate has preserved sites and relics for several thousand years.Some relics are as good as they were centuries ago.